How e-commerce capabilities in retail industry drive competitive advantage (case study of «X5 Group»)
Gazizova V.R.1![]()
1 University of International Business and Economics, ,
Скачать PDF | Загрузок: 18
Статья в журнале
Экономика, предпринимательство и право (РИНЦ, ВАК)
опубликовать статью | оформить подписку
Том 13, Номер 7 (Июль 2023)
Эта статья проиндексирована РИНЦ, см. https://elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=54310339
Аннотация:
This article explores how information technologies impact Michael Porter\\\\\\\'s framework for analyzing competitive strategy. It reassesses Porter\\\\\\\'s concepts in light of emerging technologies like cloud computing and online marketplaces. The study comprehends the transformative effects of these technologies on business processes, efficiency, and customer engagement. It includes a case study of X5 Group, evaluating its competitive advantage using Porter\\\\\\\'s Five Forces and value chain analysis. The findings inform businesses adapting to the changing competitive landscape, emphasizing the need to understand technology\\\\\\\'s impact on strategy for maintaining a competitive edge. This article is valuable for researchers, practitioners, and industry professionals interested in strategic management, information technologies, and FMCG e-commerce.
Ключевые слова: Information technologies, X5Group, chat GPT, Value Chain Analysis, Competitive Advantage
JEL-классификация: M20, O30, M10
Introduction. The use of information technologies has revolutionized the business landscape, leading to disruptions in existing models and the emergence of new ones. This has raised questions about the applicability of traditional frameworks, such as Michael Porter's Five Forces analysis [1], in understanding the competitive environment.
The existing body of literature recognizes the profound influence of information technologies on business operations, as evidenced by notable studies conducted by Michael E. Porter, Victor E. Millar [2] and Nigel Vaz [9]. However, it is still crucial to evaluate the ongoing relevance of Porter's framework in light of emerging technologies such as cloud computing and online marketplaces.
The evolving business landscape calls for an examination of the impact of information technologies on Porter's framework, specifically regarding competitive strategy analysis. This research addresses the gap in understanding how Porter's Five Forces analysis and value chain analysis adapt to new technological trends.
The primary aim of this study is to evaluate the influence of information technologies on Porter's framework for analyzing competitive strategy. It seeks to determine the continued relevance and applicability of Porter's Five Forces analysis and value chain analysis in the era of new technologies.
This article presents a case study of X5 Group, a major player in the FMCG e-commerce industry in Russia, to assess the company's competitive advantage using Porter's framework. The study offers insights into how businesses adapt their strategies to leverage new technologies for enhanced efficiency and customer engagement.
The hypothesis posits that the emergence of new technologies has disrupted traditional business models and reshaped the competitive landscape. The study expects to find that X5 Group has effectively adapted to these changes, leveraging new technologies to develop a competitive advantage.
The study employs qualitative and quantitative methods, including Porter's Five Forces analysis and the Value Chain analysis, to evaluate the impact of information technologies on X5 Group's competitive advantage and strategic positioning.
Research findings. Our study commences by offering a comprehensive definition of competitive advantage, as it serves as the fundamental concept in establishing a company's success. Competitive Advantage introduces the concept of the value chain, a general framework for thinking strategically about the activities involved in any business and assessing their relative cost and role in differentiation [1]. The focus of Competitive Advantage is on the firm, with a particular emphasis on the concept of the value chain. To fully comprehend the theory of competitive advantage, it is necessary to start by examining the value chain framework. This framework allows firms to analyze their competitive advantage and the activities that contribute to it.
Competitive advantage is derived from the various activities that a company performs in designing, producing, marketing, delivering, and supporting its products. These activities can have a significant impact on a company's relative cost position and serve as a basis for differentiation. A firm's competitive advantage, whether based on cost or differentiation, is closely tied to its value chain. However, it's important to note that the value chain is part of a broader value system, and understanding a company's ability to integrate into this system is crucial. (pic. 1)
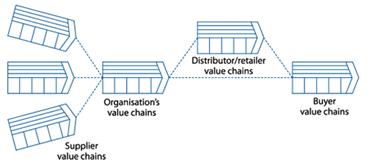
Picture 1. The value system
Source: compiled by the authors according to: [1]
Porter in his concept of the value chain, divides the activities of the company into two categories: "supportive" and "primary" activities. Furthermore, the specific activities in each category vary by industry. (pic. 2)
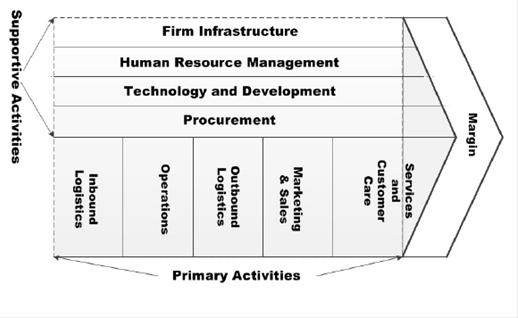
Picture 2. The Value Chain
Source: compiled by the authors according to: [1]
Michael E. Porter's concept of the value chain categorizes a company's activities into two main types: "primary" and "supportive." These activities differ by industry and are vital for businesses to add value and gain competitive advantage. Primary activities consist of five essential components: inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, marketing and sales, and services and customer care. On the other hand, supportive activities are ancillary and help primary activities become more efficient. These activities are typically labeled as overheads in a company's profit and loss statemen.
In recent years, the implementation of information technology has revolutionized the understanding of primary and supportive activities, leading to changes in the way businesses operate. Tables 3 and 4 outline primary and supportive activities from a technological perspective. (table 3, table 4)
|
Primary activity
|
Description (from
technological perspective)
|
|
Inbound
logistics
|
Automatic
warehouse management
|
|
Operations
|
Flexible
Manufacturing
|
|
Outbound
logistics
|
automatic
Order Processing
|
|
Marketing
& Sales
|
Online
marketing and point-of-sale (POS)
|
|
Services
and customer care
|
Remote
and computer-aided services
|
Source: compiled by the authors according to: [2]
|
Supportive activity
|
Description (from
technological perspective)
|
|
Procurement
|
Online
Procurement of Parts
|
|
Technology
and Development
|
Electronic
market research and computer-aided design
|
|
Human
Resource Management
|
Automated
Personnel scheduling
|
|
Firm
Infrastructure
|
Planning
models
|
Source: compiled by the authors according to: [2]
Information technology has become an integral part of the value chain and has expanded the scope of enterprise competition, creating new competitive advantages. Computer technology offers numerous benefits to businesses, such as changing industry structure, assisting with cost and differentiation strategies, and creating new business opportunities. However, competitive advantage does not come from technological capabilities alone: it comes from an integrated set of capabilities, what you are able to create with those capabilities, and a culture that embraces change [9].
The importance of information technology varies greatly across industries, and Michael E. Porter and Victor E. Millar created the Information Intensity Matrix to measure the information intensity of the value chain and information content of the product. Based on this, it can be assumed that the FMCG Retail industry has a high information intensity of the value chain and low information content of the product. (pic. 3.)
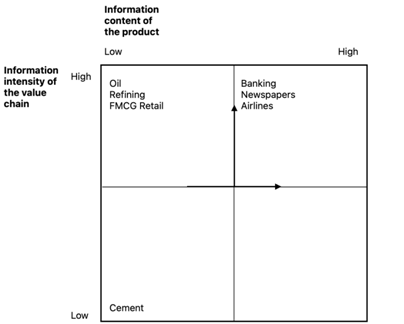
Picture 3. The position of FMCG Retail industry in information intensity matrix
Source: compiled by the authors according to: [2]
The theory of five forces, which is also introduced by Porter, helps to explain the competitive landscape of an industry. This model identifies five key forces that affect competition within an industry and outlines the factors that companies need to consider to stay ahead of the game. (pic. 4.)
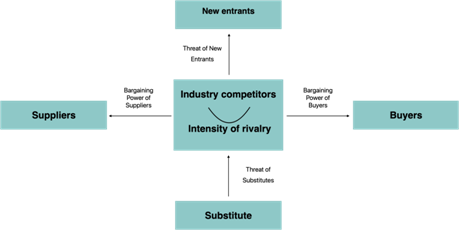
Picture 4. Porter’s five forces
Source: compiled by the authors according to: [1]
Main five forces according to Porter are:
1) Bargaining Power of Buyers:
The first force is the bargaining power of buyers, which refers to the ability of customers to affect the price and quality of products or services in the market. The determinants of this force include the concentration of buyers versus firms, buyer volume, buyer switching costs relative to firm switching costs, buyer information, and the ability to integrate backward. Additionally, the price sensitivity of buyers is also considered, which includes the total purchases made, product differences, brand identity, impact on quality, buyer profits, and decision makers' incentives.
2) Threat of New Entrants:
The second force is the threat of new entrants, which examines the barriers that prevent new companies from entering the market. The determinants of this force include economies of scale, proprietary product differences, brand identity, capital requirements, access to distribution, absolute cost advantages, government policy, expected retaliation, and exit barriers.
3) Threat of Substitute Products or Services:
The third force is the threat of substitute products or services, which refers to the extent to which customers may switch to alternatives if a company raises its prices or reduces its quality. The determinants of this force include the relative price of substitutes and the buyer propensity to substitute.
4) Bargaining Power of Suppliers:
The fourth force is the bargaining power of suppliers, which looks at the ability of suppliers to raise prices or reduce the quality of goods or services. The determinants of this force include the differentiation of inputs, switching costs of suppliers and firms in the industry, presence of substitute inputs, supplier concentration, the importance of volume to the supplier, cost relative to total purchases in the industry, impact of inputs on cost or differentiation, and the threat of forward or backward integration by firms in the industry.
5) Intensity of Rivalry Among Competing Firms:
The fifth and final force is the intensity of rivalry among competing firms in the industry, which examines the level of competition and its impact on profitability. The determinants of this force include industry growth, fixed costs, intermittent overcapacity, product differences, concentration and balance, informational complexity, diversity of competitors, and corporate stakes.
Following an in-depth exploration of the theoretical background, our study will shift its focus towards analyzing the FMCG Retail industry in Russia and the positioning of "X5 Group" among other firms.
Competitiveness is a relative characteristic, that is why it is highly important to analyze the whole industry for better understanding competitive advantage of e-commerce retailer «X5Group».
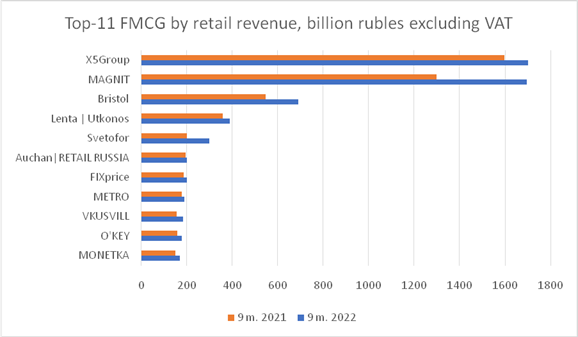 Picture
5. Top-11 FMCG by retail revenue, billion
rubles excluding VAT
Picture
5. Top-11 FMCG by retail revenue, billion
rubles excluding VAT
Source: compiled by the authors according to: [3]
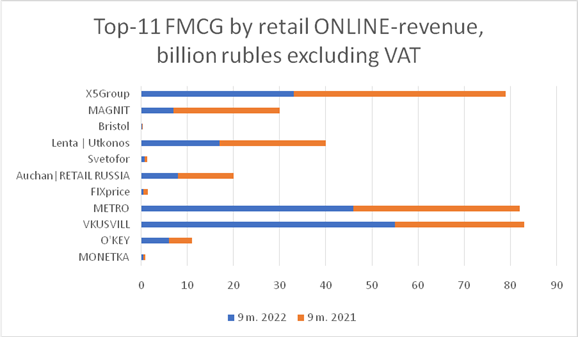 Picture
6. Top-11 FMCG by retail ONLINE-revenue,
billion rubles excluding VAT
Picture
6. Top-11 FMCG by retail ONLINE-revenue,
billion rubles excluding VAT
Source: compiled by the authors according to: [3]
The ratings above provide the information about revenue of TOP-11 leading Russian FMCG omnichannel Retail companies and their share of online sales for the period of the first nine months of 2021 and 2022 years respectively.
The industry leader, «X5Group» has a low online sales indicator of only 2.4% through its own delivery service. «X5Group» offers online purchases through its website and has its own apps in both the App Store and Google Play. In the third and fourth quarter of 2022, «X5Group» formed partnerships with «Sbermarket», «Delivery Club», and «Yandex Food», the three largest food and grocery delivery services in Russia.
«VKUSVILL» and «METRO» have the highest rate of online sales, 35% and 31% respectively. The amount of their online sales is even bigger than that of the leader of the industry «X5Group».
The next step is that we will do a complex analysis of «X5Group», thereby demonstrating a new approach of Porter’s ideas.
|
Threat
of new entrants - Low
|
The
arrival of American or European companies on the Russian market is unlikely
due to sanctions policy.
The crisis of 2022 will continue into the current year. More new retail store in formats of discounters, hard discounters and convenience stores will emerge. |
|
Threat
of substitute products and services - High
|
There
are many types of products and services «X5Group» is offering today that
other stores can offer. A lot of retailers produce their own brand products
to reduce prices.
|
|
Bargaining
power of «X5Group» buyer - High
|
The
risk is extremely high because of the ability of buyers to evaluate instantly
the prices of different suppliers in the internet via mobile phones. It has
become possible after the appearance of aggregators such as «Sbermarket», «Delivery
Club», and FMCG retail delivery services.
|
|
Bargaining
power of suppliers - moderate
|
Contracts and positive relationships bring relatively low bargaining
power of suppliers. For example, «X5 Group» began to cooperate with more than
1,100 Russian suppliers in 2022 [14].
|
|
Rivalry
among the already existing similar firms - High
|
Retail
businesses are quite aggressive in relation to each other due to strong
competition at the market. The strongest competitor of «X5Group» is «MAGNIT».
«VKUSVILL» and «METRO» have also an intensively growing e-commerce expansion.
|
Source: compiled by the authors according to: [14]
|
Inbound
Logistics
|
1) In
2018 in order to offer its customers unique imported goods at the best prices
and in compliance with all quality standards, a specialized division «X5
Import» was created. «X5 Import» is actively increasing direct supplies from
other countries. The development of own imports of goods that are not
produced in Russia, and seasonal vegetables and fruits is one of the
strategic directions of «X5 Group».
2) Warehouses for storing goods: 1. "Center" hub in Noginsk 2. "North" hub in St. Petersburg 3. "Ural" hub in Yekaterinburg 4. "South" hub in Novorossiysk 3) Warehouses are equipped with the necessary equipment for storing vegetables and fruits, as well as a dry warehouse for groceries, alcohol and non-food products. 4) «X5 Import» already works with more than 1500 suppliers from more than 60 countries, such as: Ecuador, Turkey, Egypt, China, Armenia, Belarus, Israel, Italy, Spain, South Africa, countries of the Eurasian Economic Union and others. 5) «X5 Import» has a target supplier interaction model. In this model, «X5 Import» partners grow fruits and vegetables specifically for the needs of «X5», in accordance with the requirements for quality, volume and on time. «X5 Import» works directly with manufacturers. |
|
Operations
|
1) «X5Group»
has three chain of stores: «Pyaterochka» (store near to home); «Perekrestok»
(supermarket); «Chizhik» (hard discounter).
2) Most of the services and solutions for planning and controlling the operation of the company's own and hired vehicles are based on artificial intelligence technologies and big data advanced analytics. |
|
Outbound
Logistic
|
1)
«X5 Digital» oversees the express
delivery technology platform, the infrastructure of small express delivery
dark stores and large dark stores under the «Vprok.ru» brand.
|
|
Marketing
& Sales
|
1) «X5
Media» consists of the «Food.ru» website, a mobile application and groups on
social networks. In total, the audience is more than 11 million people a
month. «Food.ru» is not a classic media project, the name Shoppable Media is
more suitable for it.
2) In 2022, total net revenue increased by 18.3% to 2.6 trillion RUB, while net offline revenue of «Pyaterochka» and «Perekrestok» increased by 18.0% and 8.3% compared to the previous year respectively. 3) Net revenue of «X5» digital business increased by 46.6% to 70.4 billion RUB compared to the previous year, with express delivery, «Vprok.ru» online hypermarket and ready-to-eat food service demonstrated strong GMV growth in 2022. |
|
Services
|
1) Customer
service department for work with suppliers, where any questions on
interaction are sorted out, for example, on efficiency, service, etc.
2) «5Post» is a delivery service. «5Post» delivers packages of «AliExpress», «Beru», «Ozon», «M.Video-Eldorado», «iHerb», «Beeline», «DNS», «Wildberries» and many other stores and marketplaces. The place of receipt of the parcel is «Pyaterochka» and «Crossroads». 3) In 2021, the «5Post» mobile application was released, which is designed to help track the status of shipments and manage the delivery of your parcels. |
Source: compiled by the authors according to: [18]
|
Procurement
|
1) Implemented
a system for the use of electronic waybills in the circuit of domestic
transportation by own transport.
2) Mutual settlements are made through the electronic data interchange (EDI) system for the purchase of spare parts, consumables and services. 3) The exchange of electronic documents with fuel companies, including the exchange of data on refueling in real time, is being implemented. 4) An e-insurance service for freight transport is being implemented. 5) A personal account for drivers is being implemented. |
|
Technology
and Development
|
1) «Dialog.X5
Insights» is a specialized division which engaged in research and development
(R&D) processes of the company. «Dialog.X5 Insights» is a
"live" analytical product. Based on vendor feedback, new report
types, data slices, and metrics are added regularly.
2) «Dialog.X5 Insights» offers users more than 15 types of reports that help them understand how consumption is changing in the network and in the category, what competitors offer and how they do it. For example, cascading decision trees (CDTs) help a supplier identify the key factors that influence a purchase decision. Based on these data, the assortment and pricing are optimized. 3) The supplier also can select a segment of buyers according to any criterion, depending on the business task, and send a sample to the audience through «5Post» distribution points or «Vprok.ru Perekrestok» delivery. After that, a post-campaign analysis is carried out, as well as a qualitative analysis of changes in consumption through customer surveys. 4) Suppliers can subscribe to digests - summary reports on category diagnostics, sources of sales, customer migration and repertory purchases and receive periodic updates if they do not need to constantly monitor metrics quickly. |
|
Human
Resource Management
|
1) Approximately
1,300 people throughout the company are engaged in the HR function. X5 is
actively implementing digital tools to get rid of repetitive transactional
work. HR processes are transferred to the multifunctional CSC (common service
center) - office management, basic operational HR analytics etc. An automated
personnel management system which was introduced in «Pyaterochka» is
implemented in every division.
2) Approximately 80% of employees are appointed internally. Only internal candidates become store directors. As for the level of middle management, there are 49% of internal appointments. 3) Well-being program was implemented for all levels of staff, and all levels within the organization. |
|
Firm
Infrastructure
|
1)
«X5 Group» has adopted a two-tier
corporate governance system, which includes the Supervisory Board and
Management.
|
Source: compiled by the authors according to: [3]
In the late 1970s, Michael Porter developed a framework for analyzing competitive strategy in the business world. His ideas were revolutionary at the time and provided a comprehensive approach to understanding how companies could gain a competitive advantage in their respective industries. However, with the advent of information technologies, Porter’s ideas should be reviewed.
Companies are now able to leverage technology to create new products and services such as cloud computing and online marketplaces. These new business models have changed the way companies compete with each other, forcing managers to look at Porter’s framework from another angle.
Information technologies are changing the value chain model in several ways, from streamlining processes and increasing efficiency to creating new opportunities for customer engagement.
By automating certain processes and utilizing data-driven insights, companies can reduce costs and improve their overall performance. For example, using predictive analytics can help companies anticipate customer needs and provide more personalized services. Additionally, cloud computing allows businesses to access data from anywhere in the world, enabling them to make decisions faster and respond quickly to customer requests.
Another way that information technologies are changing the value chain model is by creating new opportunities for customer engagement. Companies can either now create their own social media as it did X5Group or use already existing social media platforms such as Telegram and YouTube to interact with customers in real-time and build relationships with them.
With the rise of chatbots and artificial intelligence (AI) technology, firms are now able to provide customers with more personalized experiences than ever before. One of the most promising developments in this area is chat GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer), which is a type of AI that can generate natural language responses to customer inquiries. It can help businesses automate certain tasks such as order processing or product returns. By automating these processes, businesses can save time and money while still providing excellent customer service. This technology has the potential to revolutionize e-commerce by providing businesses with the ability to focus on other areas such as marketing or product development instead of mundane tasks like order processing or returns management.
Overall, it is clear that information technologies have had a significant impact on Porter’s Five Forces and The Value Chain model. By streamlining processes, creating new opportunities for customer engagement, and providing valuable insights into customer behavior, these technologies have enabled businesses to become more efficient and successful than ever before. Businesses continue to adopt new technologies, that is why it will be important for them to understand how these changes will affect their competitive environment so they can adjust their strategies accordingly in order to maintain a competitive edge.
Conclusions. «X5Group» is a market leader in the industry of online and offline FMCG retail. It has successfully implemented the most modern technologies that brought a sustainable competitive advantage. Nevertheless, a rapidly changing world facing more and more new challenges for business. «X5Group» will have to improve and develop already existing departments: from upgrading the supply chain management to building the brand awareness of «Food.ru» service among customers. Moreover, «X5Group» is planning to enter Far Eastern market, where a lot of strong players, such as «Sambery», «Ambar», «Remi» have been existing for many years. Yet «X5Group» is a leader of industry, who has a lot of stores in different segments, so it must be able to stand up to competition and maintain position in the market.
«X5Group» has become one of the most successful e-commerce companies in their industry, other e-commerce firms should look to «X5Group» as an example of how to succeed in the ever-changing digital landscape. «X5Group» have implemented cutting-edge technologies such as AI-driven product recommendations and automated order fulfillment systems that make shopping with them a breeze. These and other technologies have allowed them to retain a competitive advantage and provide customers with an enjoyable shopping experience.
Technology continues to evolve at an ever-increasing rate, that is why it is essential for e-commerce companies to stay ahead of the curve by investing in the latest information technologies available in order to remain competitive in today’s digital world.
Источники:
2. Porter Michael E., Millar Victor E. How Information Gives You Competitive Advantage. , 1985.
3. Quarterly review "Rating INFOLine E-grocery Russia TOP". [Электронный ресурс]. URL: https://infoline.spb.ru/shop/periodicheskie-obzory/page.php?ID=162476 (дата обращения: 15.05.2023).
4. Грехова Н. Мы ушли в стратегию максимальной открытости с поставщиками. Официальный сайт компании X5. [Электронный ресурс]. URL: https://www.x5.ru/ru/publication/natalya-grehova-perekryostok-my-ushli-v-strategiyu-maksimalnoj-otkrytosti-s-postavshhikami/?highlight=%22логистика%22 (дата обращения: 15.05.2023).
5. Единственным драйвером роста в форматах супермаркет и гипермаркет является online, считают в INFOLine. Официальный сайт компании Retail.ru. [Электронный ресурс]. URL: https://www.retail.ru/rbc/pressreleases/edinstvennym-drayverom-rosta-v-formatakh-supermarket-i-gipermarket-yavlyaetsya-online-schitayut-v-in/ (дата обращения: 15.05.2023).
6. Colin Combe. Introduction to E-business Management and strategy. 2006. рp. 234-237, 308-310, 310-312
7. Stephen Drew E-business Research Practice Towards an Agenda, 2002. [Электронный ресурс]. URL: https://academic-publishing.org/index.php/ejbrm/article/view/1162/1125 (дата обращения: 15.05.2023).
8. Exploiting the Virtual Value Chain. [Электронный ресурс]. URL: https://hbr.org/1995/11/exploiting-the-virtual-value-chain (дата обращения: 15.05.2023).
9. Nigel Vaz Digital Business Transformation: How Established Companies Sustain Competitive Advantage From Now to Next. - 2020.
10. Официальный сайт X5 group. [Электронный ресурс]. URL: https://www.x5.ru/ru/investors/presentations/ (дата обращения: 15.05.2023).
11. Официальный сайт X5 group. [Электронный ресурс]. URL: https://www.x5.ru/ru/publication/vitalij-dyrdasov-5post-v-2022-godu-kolichestvo-dostavok-v-postamaty-uvelichilos-na-14/?highlight=%22логистика%22 (дата обращения: 15.05.2023).
12. Официальный сайт X5 group. [Электронный ресурс]. URL: https://www.x5.ru/ru/publication/nikolaj-shestakov-x5-media-auditoriya-food-ru-prevyshaet-11-mln-chelovek-v-mesyacz/?highlight=%22маркетинг%22 (дата обращения: 15.05.2023).
13. Официальный сайт X5 group. [Электронный ресурс]. URL: https://www.x5.ru/ru/about/corporate-governance/?highlight=%22Управление%20человеческими%20ресурсами%22 (дата обращения: 15.05.2023).
14. Официальный сайт X5 Group began to cooperate with more than 1,100 Russian suppliers in 2022. [Электронный ресурс]. URL: https://www.retail.ru/news/x5-group-nachala-sotrudnichat-s-bolee-1-100-rossiyskimi-postavshchikami-v-2022-g-1-fevralya-2023-225236/ (дата обращения: 15.05.2023).
15. Официальный сайт X5 Import. [Электронный ресурс]. URL: https://www.x5.ru/ru/partners/x5-import/ (дата обращения: 15.05.2023).
16. Big data has no value without correct analytics and further implementation in business. [Электронный ресурс]. URL: https://www.x5.ru/ru/publication/elina-lopatyuk-x5-bolshie-dannye-ne-imeyut-czennosti-bez-korrektnoj-analitiki-i-dalnejshej-implementaczii-v-biznes/?highlight=%22логистика%22 (дата обращения: 15.05.2023).
17. Официальный сайт HR. [Электронный ресурс]. URL: https://www.retail.ru/interviews/tatyana-krasnopyerova-x5-group-lyudi-ne-sluchayno-prikhodyat-v-riteyl-im-nravitsya-temp-biznesa-/ (дата обращения: 15.05.2023).
18. Презентация для инвесторов. X5 Group. [Электронный ресурс]. URL: https://www.x5.ru/ru/investors/presentations/ (дата обращения: 06.06.2023).
Страница обновлена: 04.01.2026 в 23:57:44
Download PDF | Downloads: 18
How e-commerce capabilities in retail industry drive competitive advantage (case study of «X5 Group»)
Gazizova V.R.Journal paper
Journal of Economics, Entrepreneurship and Law
Volume 13, Number 7 (July 2023)
Abstract:
This article explores how information technologies impact Michael Porter's framework for analyzing competitive strategy. It reassesses Porter's concepts in light of emerging technologies like cloud computing and online marketplaces. The study comprehends the transformative effects of these technologies on business processes, efficiency, and customer engagement. It includes a case study of X5 Group, evaluating its competitive advantage using Porter's Five Forces and value chain analysis. The findings inform businesses adapting to the changing competitive landscape, emphasizing the need to understand technology's impact on strategy for maintaining a competitive edge. This article is valuable for researchers, practitioners, and industry professionals interested in strategic management, information technologies, and FMCG e-commerce.
Keywords: Information technologies, X5Group, chat GPT, Value Chain Analysis, Competitive Advantage
JEL-classification: M20, O30, M10
References:
Exploiting the Virtual Value Chain. Retrieved May 15, 2023, from https://hbr.org/1995/11/exploiting-the-virtual-value-chain
Nigel Vaz Digital Business Transformation: How Established Companies Sustain Competitive Advantage From Now to Next (0).
Porter Michael E. (1998). Competitive Advantage: Creating and Sustaining Superior Performance
Porter Michael E., Millar Victor E. (1985). How Information Gives You Competitive Advantage
Quarterly review "Rating INFOLine E-grocery Russia TOP". (in Russian). Retrieved May 15, 2023, from https://infoline.spb.ru/shop/periodicheskie-obzory/page.php?ID=162476
Stephen Drew E-business Research Practice Towards an Agenda, 2002. Retrieved May 15, 2023, from https://academic-publishing.org/index.php/ejbrm/article/view/1162/1125
