Methodological analysis of the composition of innovation management: competences and the impact of its elements on innovation performance
Hu Guiyu1![]()
1 RUDN University, Россия, Москва
Скачать PDF | Загрузок: 43
Статья в журнале
Вопросы инновационной экономики (РИНЦ, ВАК)
опубликовать статью | оформить подписку
Том 12, Номер 1 (Январь-март 2022)
Эта статья проиндексирована РИНЦ, см. https://elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=48333793
Аннотация:
The purpose of this article is to analyze the main components of the innovation management competence of high-tech enterprises, and the influence of different competence variables on the innovation performance of high-tech enterprises.
Most of previous research focuses on the impact of innovation management on innovation performance. Few studies have analyzed the specific components of innovation management competence, and almost no research has conducted empirically analyzed about the contribution of different innovation management competence to innovation performance.
On the basis of previous research, this article proposes five variables that constitute the innovation management competence of enterprises, and establishes five hypotheses to demonstrate that the five variables have a significant impact on innovation performance.
206 valid data were collected through questionnaire survey of high-tech enterprises. Factor analysis was carried out through SPSS25 to verify the factor composition of different variables and their contribution to the innovation performance of high-tech enterprises. The research results show that innovation strategic management competence, innovation organizational culture, innovation organizational structure, innovation knowledge management competence, and innovation project management competence all have a significant positive impact on innovation performance.
Scholars who are interested in research on innovation management of high-tech enterprises, the composition of innovation management competences, and enterprise innovation performance can obtain useful information from this article. This paper has an important reference for high-tech enterprises to improve their innovation management competences and improve their innovation performance.
Ключевые слова: innovation management, high-tech enterprises, innovation management competence, innovation performance, multiple linear regression analysis
Финансирование:
This paper has been supported by the RUDN University Strategic Academic Leadership Program.
JEL-классификация: O31, O32, O33, L26, M11, M21
INTRODUCTION
The main research purpose of this paper is to clarify the constituent factors of innovation management competence and the influence of different factors on innovation performance.
Through the questionnaire survey of high-tech enterprises, 206 valid data were collected, and factor analysis was carried out through SPSS25 to verify the factor composition of different variables and their contribution to the innovation performance of high-tech enterprises, and to clarify the composition system of innovation management competences.
Most of previous researches are still in the theoretical stage, and the main research content focuses on the importance of innovation management and the impact of innovation management on innovation performance. Few studies have analyzed the specific components of innovation management competence, and the specific content of different factors. Almost no studies have empirically analyzed the contribution of different innovation management competence factors to innovation performance through actual data.
For companies that want to truly improve their innovation management competences, needs to clarify the specific composition of innovation management competences and the contribution of different elements to the improvement of innovation management competences, to realize the optimal allocation of invested innovation resources.
In the first part of this paper, on the basis of previous research the author puts forward five hypotheses, namely, innovative strategic management competences, innovative organizational culture, innovative organizational structure, innovative knowledge management competences, innovative project management ability have a significant positive impact on innovation performance
The second part mainly focuses on the design of the questionnaire, including how to develop the scale, and clarifies the variable composition and measurement of innovation management ability, and conducts a descriptive statistical analysis of the collected questionnaires.
In the third and fourth part of this paper, by using SPSS 25.0 to carry out the data analysis of the relationship between innovation management ability and innovation performance, firstly, the author analyzes the reliability and validity of the questionnaire, then performs factor analysis on the variables to find out the key factors. Then, the author carries out multiple regression analysis to verify the research hypothesis, clarifies the relationship between variables and innovation performance, and the contribution of different variables to innovation performance.
The research results of this paper have an important reference for high-tech enterprises to improve their innovation management competences and improve their innovation performance. The five components of innovation management competences have specific corresponding indicators and contents. Enterprises can compare their own development to identify the cause of low innovation performance or long-term lack of breakthrough growth in innovation performance. Find the shortcomings of innovation management competences and effectively improve innovation performance.
1. Methodological analysis of the composition of innovation management competences and the impact of its elements on innovation performance
Regarding the composition of innovation management competence, Mao (2006) believes that innovation management competences are composed of strategic management competences, technological innovation management competences, market demand management competences, and basic management competences [3] (Mao Wuxing, 2006). Per Sundstrom (2009) believes that except innovation strategy perspective, projects management also important. He proposed that innovation management ability consists of the ability to construct innovative organizational culture, project management ability and innovative team building ability [19] (Per Sundstrom, Annika Zika-Viktorsson, 2009). Tidd (2006) believes that innovation management competence includes a whole process of innovation strategy formation and innovation project implementation.
On the basis of previous research, this paper proposes the five key components of innovation management competence: innovation strategic management competence, innovation organizational structure, innovation organizational culture, innovation knowledge management competence, and innovation project management competence.
The primary purpose of improving innovation management competences of enterprises is to better improve innovation performance. Therefore, this paper establishes the hypothesis that each factor has a significant positive impact on innovation performance.
Innovative strategic management competences
Innovation strategic management means that the enterprise determines its mission; the leadership attaches great importance to and supports innovation, and sets the enterprise's strategic goals according to the internal and external environment and internal conditions of the organization.
Richaed Adams [1] (Adams, Bessant, Phelps, 2006) and Benn Lawson [2] (Benn Lawson, Danny Samson, 2001) put forward the variables of innovation strategic management competence when analyzing the composition of innovation management competence. The results of Mao Wuxing's empirical analysis show that there is a positive correlation between innovation strategic management competence and enterprise innovation performance [3] (Mao Wuxing, 2006).
Therefore, this study establishes the following assumptions:
Hypothesis 1: Innovation strategic management competence has a significant positive impact on innovation performance.
Innovative knowledge management competences
Stevenson proposed that the essence of knowledge management is the means and tools used to control enterprise knowledge [4] (Stevenson, Gumpert, 1985). Liu proposed that The knowledge management process includes knowledge generation, acquisition, transfer, sharing, storage, reconstruction, utilization and protection [5] (Liu Lei, Qiao Zhong, Liu Chang, 2012). Tanigawa’s research shows the specific process mainly includes knowledge collection, organization, storage, learning, assimilation and application [6] (Tanigawa, An Yufa, Liu Chang, 2011).
Gold, et al. (2001) proposed that knowledge management competence have an important influence in the technological innovation performance of enterprises [7] (Gold, Malhotra, Segars, 2001). The influence of knowledge management ability on the performance of technological innovation of enterprises presents structural changes [8] (Xie Hefeng, 2012).
Therefore, this study establishes the following assumptions:
Hypothesis 2: Innovation knowledge management ability has a significant positive impact on innovation performance.
Innovative organizational structure
The organizational structure that supports innovation and the related organizational characteristics plays an important role in the implementation of innovation strategies and the development of innovation projects.
Zhao proposed that the formalization and specialization of organizational structures can effectively improve employee's working efficiency and has a positive impact on the performance output [9] (Zhao Xiaolu, 2008).
Wang found that the higher the degree of formalization of the organizational structure, the less resistance it is to coordinate with customers and departments of the enterprise [10] (Wang Hui, Chen Jianbin, Li Yuxia, 2011). Nahm’s study shows that the formalized organizational structure, the level of horizontal integration and the efficiency of internal communication have a positive impact on enterprise performance [11] (Nahm, Vonderembse, Koufteros, 2003).
Therefore, the study established the following hypotheses:
Hypothesis 3: The organizational structure that supports innovation has a significant positive impact on innovation performance.
Innovative organizational culture
Organizational culture is the spiritual connotation of an organization's values, concepts, beliefs, and habits. Culture that supports innovation can motivate employees to innovate, and encourage employees to continuously pursue culture with an innovative spirit and a spirit of cooperation.
Feng pointed out that organizational culture has a significant positive predictive effect on innovation competence and organizational performance, and innovation competence plays a certain mediating role in the relationship between organizational culture and organizational performance [12] (Feng Cailing, 2019).
Yin’s practical study pointed out that corporate culture has a significant impact on innovation cognition, decision-making and performance. The stability of corporate culture is also crucial, and a certain intensity of organizational value orientation are conducive to the acceptance and implementation of innovation decisions [13] (Yin Chong, 2009).
Therefore, this study establishes the following assumptions.
Hypothesis 4: An organizational culture that supports innovation has a significant positive impact on innovation performance.
Innovative project management competences
Elena Huergo illustrates the impact of technology management on innovation. Technology management variables including cooperation, technical specialization level, and market demand, innovation planning, innovation monitoring, special technical personnel and so on [14] (Elena Huergo, 2006). Thamhain's study emphasizes effective communication, effective project planning and support systems, stable long-term organizational goals and priorities that influence innovation performance and innovation outcomes, and illustrates the control of design innovation processes. Mechanisms are very important [15] (Thamhain, 1990). Therefore, this study established the following hypotheses:
Hypothesis 5: Innovation project management ability has a significant positive impact on innovation performance.
Innovation management competence is a comprehensive competence, different variable of innovation management competence together promote innovation performance. Therefore, this study establishes hypotheses to prove the relationship between the main constituent variables of innovation management competence and innovation performance, analyzes the impact of variables on innovation performance.
2. Research design on the relationship between innovation management competence and innovation performance
In this study, research on the relationship between innovation management ability and innovation performance is mainly conduct through questionnaires to collected date and make analyses.
The survey process mainly adopts the methods of Email, telephone survey and direct interview. A total of 360 questionnaires were distributed in the research on high-tech enterprises, and 206 valid samples were finally obtained, with an effective rate of 57.2%.
After analyzing the composition of innovation management variables, this study developed the scale. The development of the scale was mainly based on the research literature, and the scale with high reliability and validity was selected.
Table 1
Variable composition and measurement of innovation management competence
|
Measurement Index of Innovation Strategy Management competence
|
Sources of Metric Metrics
|
|
Specifically for
the planning and management of innovation projects, monitoring changes in the
internal and external environment of innovation projects
|
Richard
Adams [1] (Adams, Bessant, Phelps, 2006),
Benn Lawson [2] (Benn Lawson, Danny Samson, 2001), Xingwu Mao [3] (Mao Wuxing, 2006), Tufan [18] (Tufan Koc, Cemil Ceylan, 2007) |
|
Corporate
executives are entrepreneurial and innovation is seen as a key factor
affecting organizational success
| |
|
The company's
technology innovation strategy supports the organization's strategy, and the
innovation strategy is shared and applied to each department and project
| |
|
Measurement Index of Innovative Knowledge Management competence
|
Sources of Metric Metrics
|
|
Innovative ideas
come from different departments of the organization and the quantity and
quality of ideas is high
|
Richard
Adams [1] (Adams, Bessant, Phelps, 2006),
Gold [7] (Gold, Malhotra, Segars, 2001), Hefeng Xie [8] (Xie Hefeng, 2012), Linjie Zhao [16] (Zhao Linjie, Tang Shukun, 2007) |
|
Constructive
ideas are evaluated, responded to and implemented if justified and innovative
ideas are supported by the incentive system
| |
|
Enterprises will
use suppliers or collaborating units, customers, rivals, universities and
research institutes to participate in innovation, and employees with special technical
skills and technical experience in the project
| |
|
Measurement Index of Innovative Organizational Structure competence
|
Sources of Metric Metrics
|
|
Frequently
communication between the various innovation project teams of the enterprise
and between departments
|
Zhao
Xiaolu [9] (Zhao Xiaolu, 2008),
Wang Hui [10] (Wang Hui, Chen Jianbin, Li Yuxia, 2011), Nahm [11] (Nahm, Vonderembse, Koufteros, 2003), Xu Qingrui [17] (Xu Qingrui, 2007), Tufan Koc [18] (Tufan Koc, Cemil Ceylan, 2007) |
|
There
are cross-departmental teams in the business for product and process
innovation
| |
|
The
enterprise has a good level of matrix management
| |
|
Enterprises
show the characteristics of learning organizations. For example, there are
channels for learning and communication, etc.
| |
|
In
team work, work is designed to encourage autonomy
| |
|
Employees
are empowered to make decisions in innovative project and have the right to
plan and control management practices.
| |
|
The
design of the corporate organizational structure encourages employees to
participate in decision-making
| |
|
Measurement Index of Innovative Organizations Cultural competence
|
Sources of Metric Metrics
|
|
Established
an incentive mechanism for innovative teams
|
Richard
Adams [1] (Adams, Bessant, Phelps, 2006),
Feng [12] (Feng Cailing, 2019), Yin [13] (Yin Chong, 2009), An Jingwen [20] (An Jingwen, Li Yuanchun, Liu Haidong, Zhen Haihong, Liang Ruiwen, 2006) |
|
The
organization has a clear vision and values for innovation, and the business
tolerates innovation failures and well-intentioned mistakes, and tolerates
risk
| |
|
Build
an atmosphere that fosters innovation, individuals with changing motivations
and challenging behaviors
| |
|
Measurement index of Innovative Project Management competence
|
Sources of Metric Metrics
|
|
Engineers
are responsible for innovation and have a responsibility to ensure the
implementation of ideas
|
Elena
Huergo [14] (Elena Huergo, 2006),
Thamhain [15] (Thamhain, 1990), Xu Qingrui [17] (Xu Qingrui, 2007), Tufan [18] (Tufan Koc, Cemil Ceylan, 2007), Per Sundstrom [19] (Per Sundstrom, Annika Zika-Viktorsson, 2009) |
|
The
organization establishes a rigorous plan and establishes milestones, while
having the flexibility to solve technical problems, considering plans based
on new perspectives and processes
| |
|
Establish
a feedback mechanism to analyze the reasons for changes
| |
|
It is
the responsibility of innovation team members to discuss changes in customer
needs through customer feedback, to continuously improve products of innovative
projects, and to find technical solutions
| |
|
Channels
and methods of information collection with innovative project development,
and a place for communication
| |
|
According to the
feedback information, make adjustments to the changes of innovation projects,
and continuously carry out predictions for future innovations
|
Innovation performance and its measurement
The measurement of innovation performance can measure the patents applied for and authorized by the company, the formulation of industry standards, and the market share of new products. Some studies suggest that innovation output can be measured by patents, including the number of patents, and the successful application of patents in a given period. Scherer’s research shows that patents are also related to the economy can measure the economic effects of patents by the profit of new products [21] (Scherer, 1988). Based on previous research on the measurement indicators of innovation performance, this study selected four indicators: the company has a satisfactory new product profit margin in the past three years, the market share of the company's new products, the company's patent applications in the past three years and in terms of the number of authorizations, the company plays a major role in the formulation of industry standards.
Descriptive statistical analysis was carried out on the obtained 206 valid sample data, and the samples of the questionnaires involved enterprises of different natures and industries, which were representative to a certain extent.
Table 2
Descriptive analysis of questionnaires
|
Enterprise
size
|
Below
100 employees
|
36.4%
|
|
Between
100–300 employees
|
23.8%
| |
|
Between
300–500 employees
|
11.2%
| |
|
Between
500–1000 employees
|
13.6%
| |
|
The
number of employees is between 1000–2000
|
9.7%
| |
|
More
than 2000 employees
|
5.3%
| |
|
Enterprise
nature
|
State-owned
|
5.82%
|
|
State
holding
|
20.9%
| |
|
Wholly
foreign owned enterprise
|
8.73%
| |
|
Collectively
owned
|
1.45%
| |
|
Private
enterprise
|
46.6%
| |
|
Mixed
ownership
|
16.5%
| |
|
Industry
|
Transformation
of traditional industries
|
36.4%
|
|
New
material technology
|
6.8%
| |
|
Electronics
and information technology
|
28.6%
| |
|
Pharmaceutical
biology
|
11.2%
| |
|
New
energy
|
8.3%
| |
|
Resource
and environmental technology
|
2.42%
| |
|
High-tech
service industry
|
5.8%
| |
|
Aerospace
|
0.48%
| |
|
R&D
investment ratio in 2021
|
R&D
investment 0–5%
|
16%
|
|
R&D
investment 5–10%
|
44.2%
| |
|
R&D
investment 10–15%
|
18%
| |
|
R&D
investment 15–30%
|
12.1%
| |
|
R&D
investment of more than 30%
|
9.7%
|
3. Empirical analysis and research conclusions of the impact of innovation management competence on innovation performance
By using SPSS 25.0 to carry out the data analysis of the relationship between innovation management ability and innovation performance, firstly, the factor analysis is carried out on the variables, and the reliability and validity of the questionnaire is analyzed to find out the key factors;
The reliability and validity of the questionnaire and the results of factor analysis
Before the factor analysis, the Bartlett test and KMO value test used in this study to determine whether the factor analysis is suitable. After factor analysis, reliability was tested using Cronbach's Alpha.
Table 3
KMO values of each measured variable and Bartlett's intensite test
|
Measure variable
|
KMO Values
|
Bartlett's test
| ||
|
Chi-square
approximation
|
Degrees of freedom
|
P-value
| ||
|
Innovative
strategic management competences
|
0.770
|
588.244
|
3
|
P<0.001
|
|
Innovative
knowledge management competences
|
0.765
|
479.106
|
3
|
P<0.001
|
|
Innovative
organizational structure
|
0.943
|
1550.052
|
21
|
P<0.001
|
|
Innovative
organizational culture
|
0.764
|
473.396
|
3
|
P<0.001
|
|
Innovative
project management competences
|
0.920
|
816.889
|
15
|
P<0.001
|
|
Innovation
performance
|
0.849
|
804.520
|
6
|
P<0.001
|
Both the KMO value and Bartlett's test passed the test, indicating that the factor analysis is suitable as it shown in table 3.
Factors analysis of the variable innovation strategic management competence
In the process of factor analysis in this paper, the factor load of the variable is greater than 0.5 as the standard, and the items that do not meet the above requirements are eliminated.
Table 4
Factor composition of innovation strategy management competence variables
|
Item
|
Factor Composition
|
|
Specifically for
the planning and management of innovation projects, monitoring changes in the
internal and external environment of innovation projects
|
0.892
|
|
Corporate
executives are entrepreneurial and innovation is seen as a key factor
affecting organizational success
|
0.900
|
|
The company's
technology innovation strategy supports the organization's strategy, and the
innovation strategy is shared and applied to each department and project
|
0.919
|
The lowest factor loading is 0.892. The explained variance of the factor is 0.90364>0.5. The Cronbach's Alpha value of the generated factor is 0.946>0.7, which indicates that the factor scale is reliable, has passed the consistency test, and has good reliability.
Table 5
Factor composition of the variables of innovative knowledge management competence
|
Item
|
Factor Composition
|
|
Innovative ideas
come from different departments of the organization and the quantity and
quality of ideas is high
|
0.878
|
|
Constructive
ideas are evaluated, responded to and implemented if justified and innovative
ideas are supported by the incentive system
|
0.877
|
|
Enterprises will
use suppliers or collaborating units, customers, rivals, universities and
research institutes to participate in innovation, and employees with special
technical skills and technical experience in the project
|
0.863
|
It can be seen from the analysis results that the lowest factor loading is 0.863, therefore all the items can be retained. The explained variance of the generation factor is 0.87299>0.5. The Cronbach's Alpha value is 0.925, which indicates that the factor table is reliable, has passed the consistency test, and has good reliability.
Table 6
Factor composition of innovative organizational structure
|
Item
|
Factor Composition
|
|
Frequently
communication between the various innovation project teams of the enterprise
and between departments
|
0.858
|
|
There
are cross-departmental teams in the business for product and process
innovation
|
0.818
|
|
The
enterprise has a good level of matrix management
|
0.854
|
|
Enterprises
show the characteristics of learning organizations. For example, there are
channels for learning and communication, etc.
|
0.777
|
|
In
team work, work is designed to encourage autonomy
|
0.723
|
|
Employees
are empowered to make decisions in innovative project and have the right to
plan and control management practices.
|
0.811
|
|
The
design of the corporate organizational structure encourages employees to
participate in decision-making
|
0.839
|
The lowest factor loading of the question term is 0.723; therefore all the question terms can be retained. The explained variance of the generation factor was 0.81136>0.5. The Cronbach's Alpha value is 0.961, which indicates that the factor table is reliable, and it has passed the consistency test, and has good reliability.
Table 7
Factor composition of innovative organizational culture
|
Item
|
Factor Composition
|
|
Established
an incentive mechanism for innovative teams
|
0.880
|
|
The
organization has a clear vision and values for innovation, and the business
tolerates innovation failures and well-intentioned mistakes, and tolerates
risk
|
0.871
|
|
Build
an atmosphere that fosters innovation, individuals with changing motivations
and challenging behaviors
|
0.862
|
The lowest factor loading is 0.880. The explained variance of the factor is 0.87100>0.5. The Cronbach's Alpha value of the generated factor is 0.923>0.7, which indicates that the factor scale is reliable, has passed the consistency test, and has good reliability.
Table 8
Factor composition of innovation project management competence variables
|
Item
|
Factor Composition
|
|
Engineers are
responsible for innovation and have a responsibility to ensure the
implementation of ideas
|
0.802
|
|
The organization
establishes a rigorous plan and establishes milestones, while having the
flexibility to solve technical problems, considering plans based on new
perspectives and processes
|
0.721
|
|
Establish a
feedback mechanism to analyze the reasons for changes
|
0.710
|
|
It is the
responsibility of innovation team members to discuss changes in customer
needs through customer feedback, to continuously improve products of
innovative projects, and to find technical solutions
|
0.714
|
|
Channels and
methods of information collection with innovative project development, and a
place for communication
|
0.721
|
|
According to the
feedback information, make adjustments to the changes of innovation projects,
and continuously carry out predictions for future innovations
|
0.618
|
The lowest factor loading of this item is 0.710; therefore all the terms can be retained. The explained variance of the generation factor is 0.71437>0.5. The Cronbach's Alpha value is 0.918, which indicates that the factor table is reliable, and it has passed the consistency test and has good reliability.
Table 9
Summary of Cronbach’s Alpha values for each measurement variable
|
Measurement variable
|
Number of questions
|
Cronbach’s Alpha Value
|
|
Innovative
strategic management competences
|
3
|
0.946
|
|
Innovative
knowledge management competences
|
7
|
0.961
|
|
Innovative
organizational structure
|
7
|
0.961
|
|
Innovative
organizational culture
|
3
|
0.923
|
|
Innovative
project management competences
|
6
|
0.918
|
|
Innovation
performance
|
4
|
0.945
|
Through factor analysis, the Cronbach's Alpha values of the five variables are all >0.7 and the overall reliability meets the requirements. Through the reliability test, the scale used in this study has a high level of reliability.
At the same time, the explained variances of each variable are all greater than 0.5, indicating that the scale has a good level of validity.
4. Innovation management and innovation performance regression analysis results
Before carrying out regression analysis, test for multicollinearity and normal distribution among variables. After passing the above test, carry out regression analysis on the variables to test the relationship between each variable and innovation performance.
Multicollinearity test
Table 10
Results of multicollinearity analysis
|
Variable
|
Tolerance Statistics
|
Variance inflation factor (VIF)
|
|
Innovative
strategic management competences
|
0.101
|
9.945
|
|
Innovative
knowledge management competences
|
0.102
|
9.848
|
|
Innovative
organizational structure
|
0.123
|
8.136
|
|
Innovative
organizational culture
|
0.128
|
7.798
|
|
Innovative
project management competences
|
0.179
|
5.596
|
When 0<VIF<10, there is no multicollinearity; when 10<VIF<100, there is strong multicollinearity; when VIF>100, there is severe multicollinearity. If the tolerance of an independent variable is less than 0.1, the collinearity problem may be serious.
It can be seen from the above table that the VIF in all models is less than 10, so there is no close linear relationship between the assumed variables. It can be seen that there is no obvious multicollinearity in this study, and regression analysis can be carried out.
Normal distribution detection
Whether the data is normally distributed can be observed by using the Q–Q chart, which compares the degree of agreement between the theoretical quantile and the actual quantile. If it obeys a normal distribution, the data points basically coincide with the theoretical straight line.
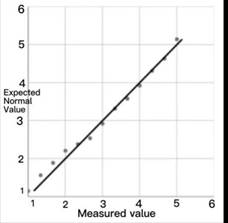
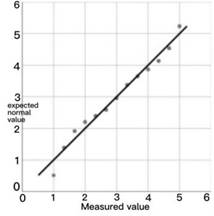
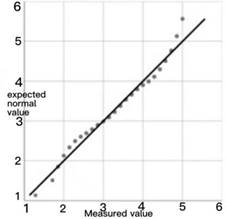




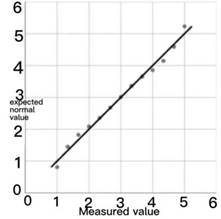
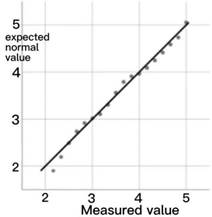

From the above normal distribution graph, we can know that the points in the graph are roughly on a straight line, so the data satisfies the normal distribution.
Variable composition of innovation management competence and innovation performance
A regression analysis was carried out on the variables of independent innovation management competence and innovation performance. The fit of the model is shown in the following table with good goodness of fit, and the results are shown in table 11. It shows that the regression relationship can explain more than 95% of the variance of the dependent variable.
Table 11
Goodness of fit of the model
|
Model
|
R
|
R Square
|
Adjusted R Square
|
|
1
|
0.979
|
0.959
|
0.958
|
Regression analysis was carried out on innovation performance, and T-test was used for the results, sig < 0.05, the test results were significant, and the original hypothesis was accepted. The regression results are shown in table 12.
Table 12
Results of regression analysis
|
Dependent
variable
|
Independent variable
|
Beta
|
T
|
Sig
|
R²
|
|
Innovation
Performance
|
Constant
|
|
0.000
|
|
0.937
|
|
Innovative
strategic management competences
|
0.269
|
5.985
|
0.000
| ||
|
innovative
organizational structure
|
0.213
|
5.231
|
0.000
| ||
|
Innovative
organizational culture
|
0.233
|
5.855
|
0.000
| ||
|
Innovative
knowledge management competences
|
0.154
|
3.442
|
0.001
| ||
|
Innovative
project management competences
|
0.152
|
4.492
|
0.000
|
The standardized partial regression coefficient is to compare the degree of influence of each variable through standard normal transformation. It can be used to directly compare the influence degree of the corresponding variable of each variable, so the coefficient of the regression equation here can be used to determine the importance and weight of the variable.
According to the results of empirical analysis, innovation strategic management competence, innovation organizational structure, innovation organizational culture, innovation knowledge management competence, and innovation project management competence all have a significant positive impact on innovation performance. The correlation coefficients between the five variables and innovation performance are shown in table 13.
Table 13
Research model of the relationship between innovation management competence and innovation performance
|
Innovation performance
| |
|
Variable
|
Correlation Coefficient
|
|
Innovative
strategic management competences
|
0.269
|
|
innovative
organizational structure
|
0.213
|
|
Innovative
organizational culture
|
0.233
|
|
Innovative
knowledge management competences
|
0.154
|
|
Innovative
project management competences
|
0.152
|
Through regression analysis, it can be seen that the influence of each component variable on innovation performance is different, and the relative importance of each component variable can be judged by the correlation coefficient.
The innovation strategy management variables show the most significant relationship with innovation performance. Therefore, organizations need to attach importance to the accumulation of knowledge, establish a knowledge transformation and learning mechanism, and at the same time carry out organizational innovation strategy management, promote the participation of project-level personnel in the formulation of organizational strategies, and ensure the sharing of innovation strategies in the organization.
The innovation organization culture has the second influence on innovation performance. A corporate culture that supports innovation can motivate employees to innovate, and encourage employees to continuously pursue excellence.
The innovation organization structure has the third influence on innovation performance. It is necessary to build a flexible and diversified organization that can promote employee participation in decision-making, empower employees to have autonomy in the organization.
Innovation knowledge management ability also has a significant impact on innovation performance. The ability to generate high-quality innovative ideas in an organization and to ensure that innovative ideas can be selected and evaluated and implemented in the organization is a major factor affecting organizational innovation performance.
Innovation project management competences also have an important impact on innovation performance. Establish flexible plans in the organization, establish milestones, and coordinate through plan implementation and meetings. At the same time, ensure that team members have a sense of responsibility for innovation, find problems, collect data, and make team members responsible for innovation through task decomposition and responsibility decomposition.
CONCLUSION
On the basis of previous research, this paper combines the theoretical analysis of innovation management competence, as well as the analysis of the connotation and status quo of innovation management competence of high-tech enterprises, puts forward five hypotheses that is five variables, namely innovation strategic management competence, innovation knowledge management competence, innovation organizational structure, innovative organizational culture and innovative project management ability, all have significant positive effects on innovation performance.
The data collection method of this study was mainly through questionnaires. The survey objects are mainly high-tech enterprises that carry out innovation activities. 206 valid data were collected through questionnaire survey.
After collecting the data, factor analysis is carried out on the variables firstly, the reliability and validity of the questionnaire are analyzed, and the key factors of each variable are found out. Secondly, use SPSS25 to carry out multiple linear regression analysis to verify the research hypothesis and clarify the contribution of different variables to innovation performance.
According to the results of empirical analysis, all five variables have a significant positive impact on innovation performance, in descending order of influence, innovation strategy management competence, innovation organizational culture, innovation organizational structure, innovation knowledge management competence, and innovation project management competence.
The research results of this paper have an important reference value for high-tech enterprises to improve their innovation management competences and improve innovation performance. The five components of innovation management competences have specific corresponding indicators and contents.
Enterprises can identify the reasons for low innovation performance or the long-term lack of breakthrough growth in innovation performance, find the shortcomings of innovation management competences, and effectively improve innovation performance.
Источники:
2. Benn Lawson, Danny Samson Developing innovation competence in organizations: a dynamic competences approach // International Journal of Innovation Management. – 2001. – № 5(3).
3. Mao Wuxing Research on Enterprise's Comprehensive Innovation Management competence: Taking China's Electronic Information Industry as an Example. / PhD Thesis. - Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2006.
4. Stevenson H., Gumpert D. The heart of entrepreneurship. - MA: Harford Business School Press, 1985. – 184 p.
5. Liu Lei, Qiao Zhong, Liu Chang Research on the cooperative game problem in the docking mode of agriculture and supermarket // Chinese Journal of Management Engineering. – 2012. – № 4. – p. 100-105.
6. Tanigawa, An Yufa, Liu Chang Research on the quality control strength in the mode of "agricultural-supermarket docking" // Soft Science. – 2011. – № 25(6). – p. 21-24.
7. Gold A.H., Malhotra A., Segars A.H. Knowledge management: An Organizational competences perspective // Journal of Management Information Systems. – 2001. – № 18. – p. 185-214.
8. Xie Hefeng The Impacts of Enterprise’s Knowledge Management competences on Technological Innovation Performance // Journal of University of South China (Social Science Edition). – 2012. – № 8. – p. 43-48.
9. Zhao Xiaolu An Empirical Study on the Organizational Structure and Performance of Enterprises. - Xidian University, 2008. – 48-50 p.
10. Wang Hui, Chen Jianbin, Li Yuxia An empirical study on the relationship between enterprise IT performance and organizational structure dimension // Management Review. – 2011. – № 5. – p. 47.
11. Nahm A.Y., Vonderembse M. A., Koufteros X. A. The impact of organizational structure on time-based manufacturing and plant performance // Journal of Operations Management. – 2003. – № 21(3). – p. 281-303. – doi: 10.1016/S0272-6963(02)00107-9.
12. Feng Cailing The influence of organizational culture on organizational performance // Ludong University. – 2019. – № 35(2). – p. 180-184.
13. Yin Chong Management Science and Engineering // Shandong University. – 2009. – № 19(1). – p. 25-36.
14. Elena Huergo The role of technological management as a source of innovation: Evidence from Spanish manufacturing firms // Research Policy. – 2006. – № 35. – p. 1377-1388.
15. Thamhain H.J. Managing technologically innovation team efforts toward new product success // Journal of Product Innovation Management. – 1990. – № 7. – p. 5-18.
16. Zhao Linjie, Tang Shukun A new technology innovation management tool - Innovation Management Maturity Model Research (IMMM) // Business. – 2007. – № 10. – p. 81-87. – doi: 168011090.
17. Xu Qingrui Comprehensive Innovation Management Theory and Practice. - Beijing: Science Press, 2007.
18. Tufan Koc, Cemil Ceylan Factors impacting the innovation capacity in large scale companies // Technovation. – 2007. – № 27. – p. 105-114.
19. Per Sundstrom, Annika Zika-Viktorsson Organizing for innovation in a product development project: Combining innovative and result oriented ways of working - A case study // International Journal of Innovation Management. – 2009. – № 27. – p. 745-753.
20. An Jingwen, Li Yuanchun, Liu Haidong, Zhen Haihong, Liang Ruiwen Research on the evaluation index system of enterprise technological innovation competence maturity // China Science and Technology Forum. – 2006. – p. 19.
21. Scherer R. A New Typology for Organizations: Market, Bureaucracy, Clan and Mission, with Application to American Denominations // Journal for the Scientific Study of Religion. – 1988. – doi: 10.2307/1386945.
Страница обновлена: 26.12.2025 в 04:12:23
Download PDF | Downloads: 43
Methodological analysis of the composition of innovation management: competences and the impact of its elements on innovation performance
Guiyu H.Journal paper
Russian Journal of Innovation Economics
Volume 12, Number 1 (January-March 2022)
Abstract:
The purpose of this article is to analyze the main components of the innovation management competence of high-tech enterprises, and the influence of different competence variables on the innovation performance of high-tech enterprises.
Most of previous research focuses on the impact of innovation management on innovation performance. Few studies have analyzed the specific components of innovation management competence, and almost no research has conducted empirically analyzed about the contribution of different innovation management competence to innovation performance.
On the basis of previous research, this article proposes five variables that constitute the innovation management competence of enterprises, and establishes five hypotheses to demonstrate that the five variables have a significant impact on innovation performance.
206 valid data were collected through questionnaire survey of high-tech enterprises. Factor analysis was carried out through SPSS25 to verify the factor composition of different variables and their contribution to the innovation performance of high-tech enterprises. The research results show that innovation strategic management competence, innovation organizational culture, innovation organizational structure, innovation knowledge management competence, and innovation project management competence all have a significant positive impact on innovation performance.
Scholars who are interested in research on innovation management of high-tech enterprises, the composition of innovation management competences, and enterprise innovation performance can obtain useful information from this article. This paper has an important reference for high-tech enterprises to improve their innovation management competences and improve their innovation performance.
Funding:
This paper has been supported by the RUDN University Strategic Academic Leadership Program.
Keywords: innovation management, high-tech enterprises, innovation management competence, innovation performance, multiple linear regression analysis
Funding:
JEL-classification: O31, O32, O33, L26, M11, M21
References:
Adams R., Bessant J., Phelps R. (2006). Innovation management measurement: A review International Journal of Innovation Management Review. (8(1)). 21-47.
An Jingwen, Li Yuanchun, Liu Haidong, Zhen Haihong, Liang Ruiwen (2006). Research on the evaluation index system of enterprise technological innovation competence maturity China Science and Technology Forum. 19.
Benn Lawson, Danny Samson (2001). Developing innovation competence in organizations: a dynamic competences approach International Journal of Innovation Management. (5(3)).
Elena Huergo (2006). The role of technological management as a source of innovation: Evidence from Spanish manufacturing firms Research Policy. (35). 1377-1388.
Feng Cailing (2019). The influence of organizational culture on organizational performance Ludong University. (35(2)). 180-184.
Gold A.H., Malhotra A., Segars A.H. (2001). Knowledge management: An Organizational competences perspective Journal of Management Information Systems. (18). 185-214.
Liu Lei, Qiao Zhong, Liu Chang (2012). Research on the cooperative game problem in the docking mode of agriculture and supermarket Chinese Journal of Management Engineering. (4). 100-105.
Mao Wuxing (2006). Research on Enterprise's Comprehensive Innovation Management competence: Taking China's Electronic Information Industry as an Example
Nahm A.Y., Vonderembse M. A., Koufteros X. A. (2003). The impact of organizational structure on time-based manufacturing and plant performance Journal of Operations Management. (21(3)). 281-303. doi: 10.1016/S0272-6963(02)00107-9.
Per Sundstrom, Annika Zika-Viktorsson (2009). Organizing for innovation in a product development project: Combining innovative and result oriented ways of working - A case study International Journal of Innovation Management. (27). 745-753.
Scherer R. (1988). A New Typology for Organizations: Market, Bureaucracy, Clan and Mission, with Application to American Denominations Journal for the Scientific Study of Religion. doi: 10.2307/1386945 .
Stevenson H., Gumpert D. (1985). The heart of entrepreneurship
Tanigawa, An Yufa, Liu Chang (2011). Research on the quality control strength in the mode of "agricultural-supermarket docking" Soft Science. (25(6)). 21-24.
Thamhain H.J. (1990). Managing technologically innovation team efforts toward new product success Journal of Product Innovation Management. (7). 5-18.
Tufan Koc, Cemil Ceylan (2007). Factors impacting the innovation capacity in large scale companies Technovation. (27). 105-114.
Wang Hui, Chen Jianbin, Li Yuxia (2011). An empirical study on the relationship between enterprise IT performance and organizational structure dimension Management Review. (5). 47.
Xie Hefeng (2012). The Impacts of Enterprise’s Knowledge Management competences on Technological Innovation Performance Journal of University of South China (Social Science Edition). (8). 43-48.
Xu Qingrui (2007). Comprehensive Innovation Management Theory and Practice
Yin Chong (2009). Management Science and Engineering Shandong University. (19(1)). 25-36.
Zhao Linjie, Tang Shukun (2007). A new technology innovation management tool - Innovation Management Maturity Model Research (IMMM) Business. (10). 81-87. doi: 168011090.
Zhao Xiaolu (2008). An Empirical Study on the Organizational Structure and Performance of Enterprises
